Introduction
A logical rule is a way to format a rule in a flow chart. This example is a very simple logical rule just to demonstrate the interface.
After creating the rule, you can test it to confirm it works as expected.
|
QUICK STEPS |
| 1 |
Open the entity |
| 2 |
Create a new logical rule |
| 3 |
Enter the rule details |
| 4 |
Click OK |
| 5 |
Drag and drop the components of the rule |
| 6 |
Enter the description and expression for each component |
| 7 |
Add variables |
| 8 |
Enter the variable details |
| 9 |
Click OK |
| 10 |
Save the rule |
| 11 |
Build the rule |
| 12 |
Add a scenario |
| 13 |
Enter the Input Value and Expected Value |
| 14 |
Run the test |
| 15 |
View the diagram |
| 16 |
Save the scenario |
Detailed Steps
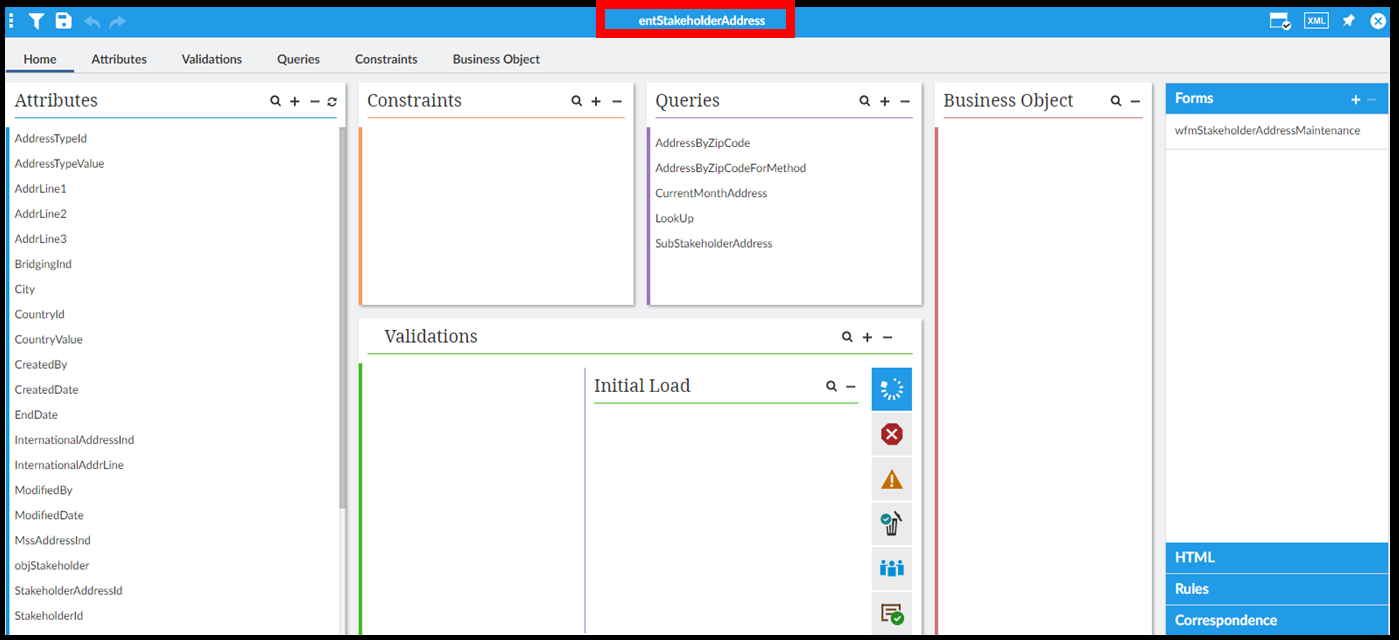
Step 1. Open the entity.
Open the entity where you want to create a logical rule.
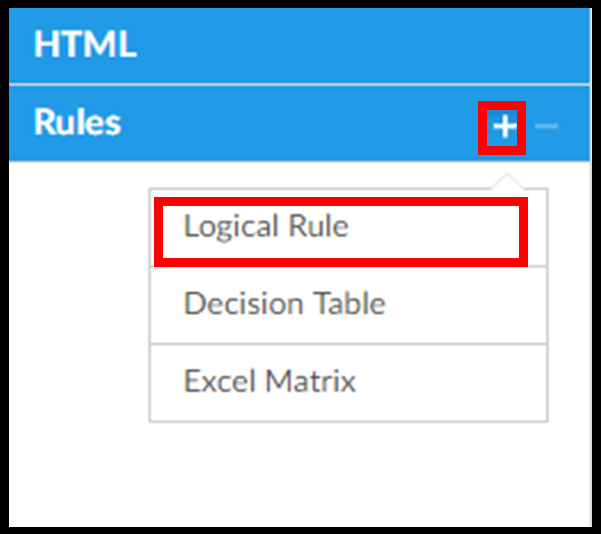
Step 2. Create a new logical rule.
In the Rules section, click the plus icon and select the type of rule you are creating. In this case, that’s a logical rule.
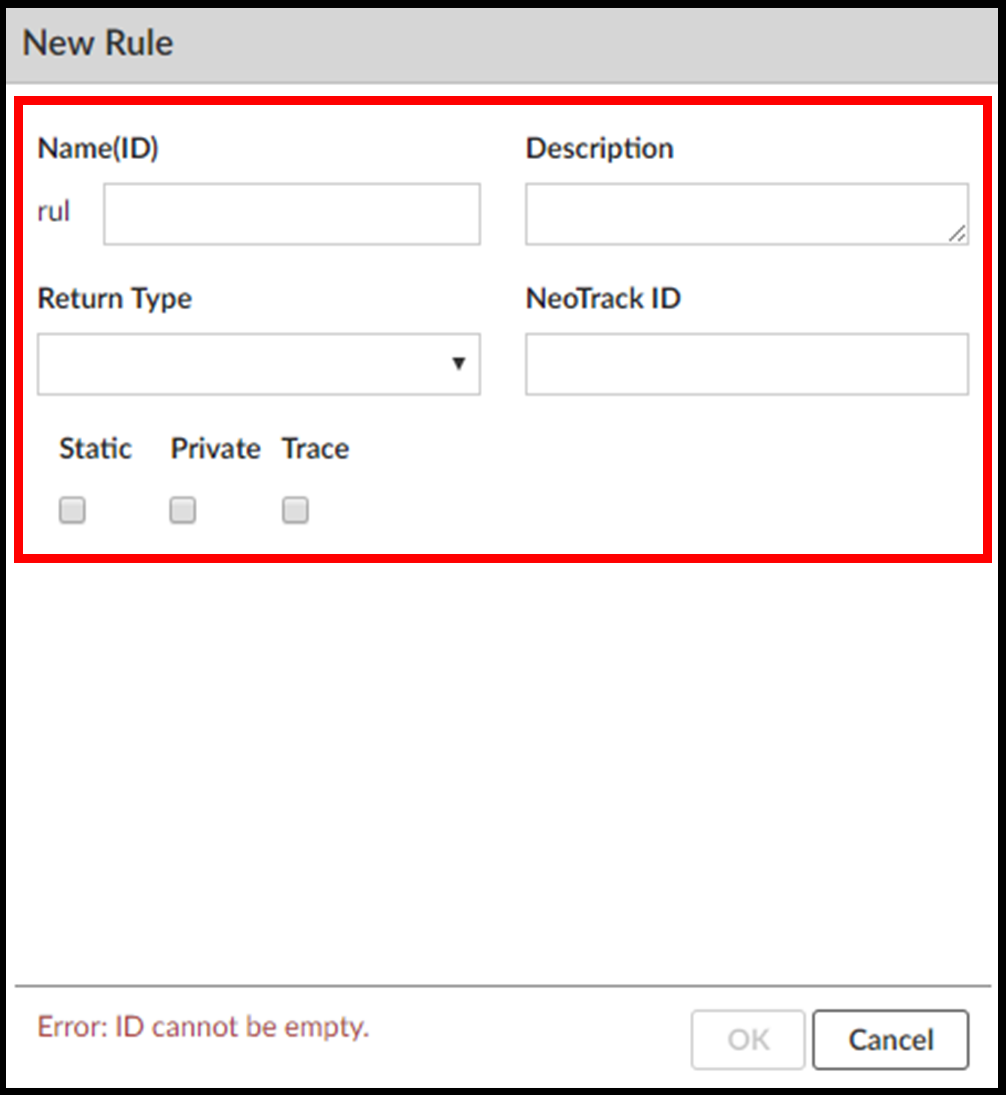
Step 3. Enter the rule details.
Enter the following properties:
- Name(ID): This is the rule’s programmatic ID. This property is required. The ID has to be unique and it cannot start with numbers.
- Description: Optionally, you can enter a short description for your rule.
- Return Type: This is the data type of the result you expect the rule to return (string, int, etc.).
- NeoTrack ID: This is the ID that Sagitec’s design documentation tool uses to refer to the rule.
- Static: If checked, the rule will be available to call from anywhere. Otherwise, you will have to call the rule from an instance of its object. In a logical rule, the entity attributes can be directly used if the rule is not static.
- Cache Result: If Static is checked, this displays. When checked, the system stores the result of the rule’s execution in the cache. The next time it runs the rule, it retrieves the result from the cache rather than re-execute the rule.
- Private: If checked, you will only be able to access the rule from the place it’s declared.
- Trace: Making a rule traceable means you can view the path and result every time the code executes that rule.
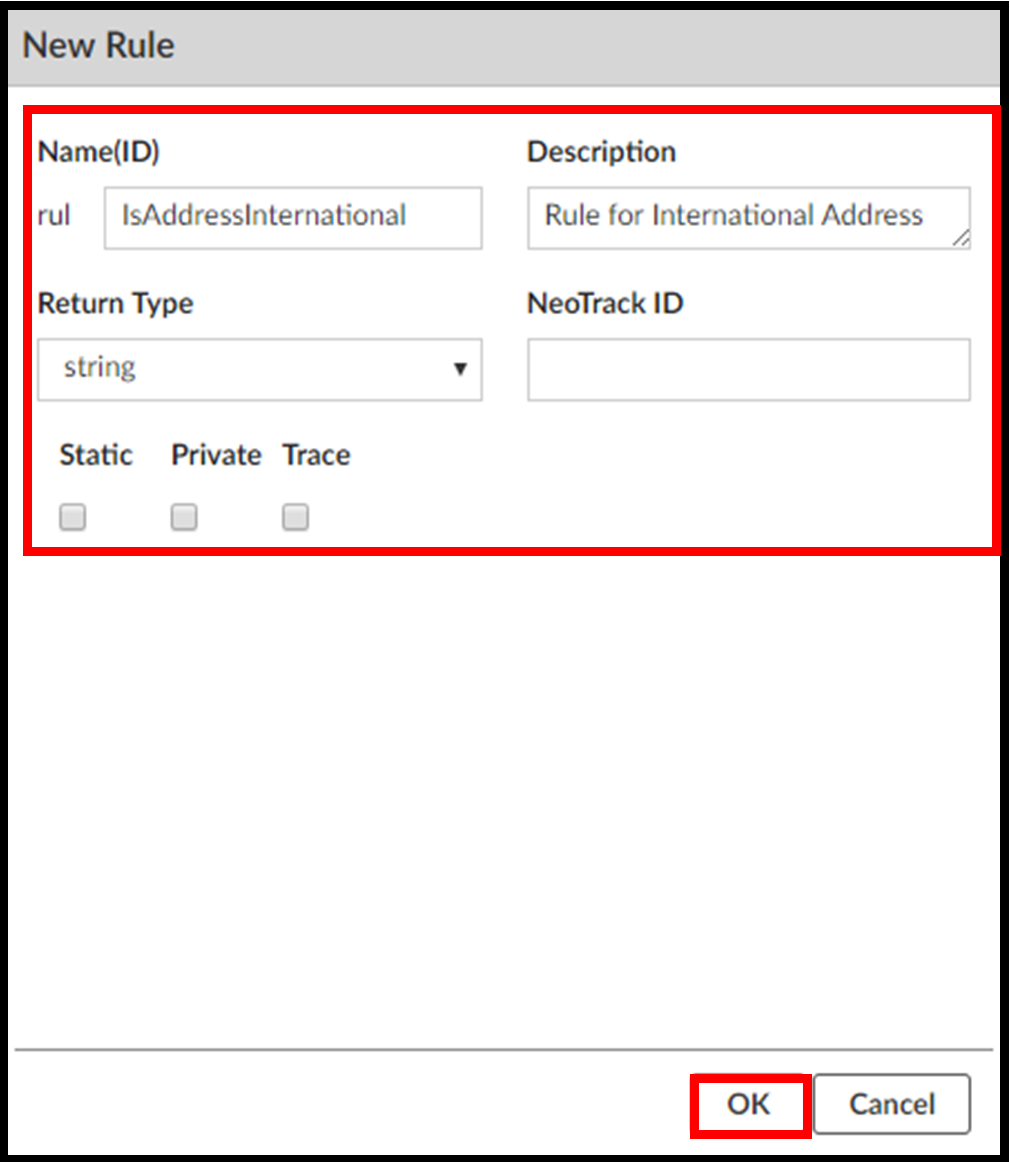
Step 4. Click OK.
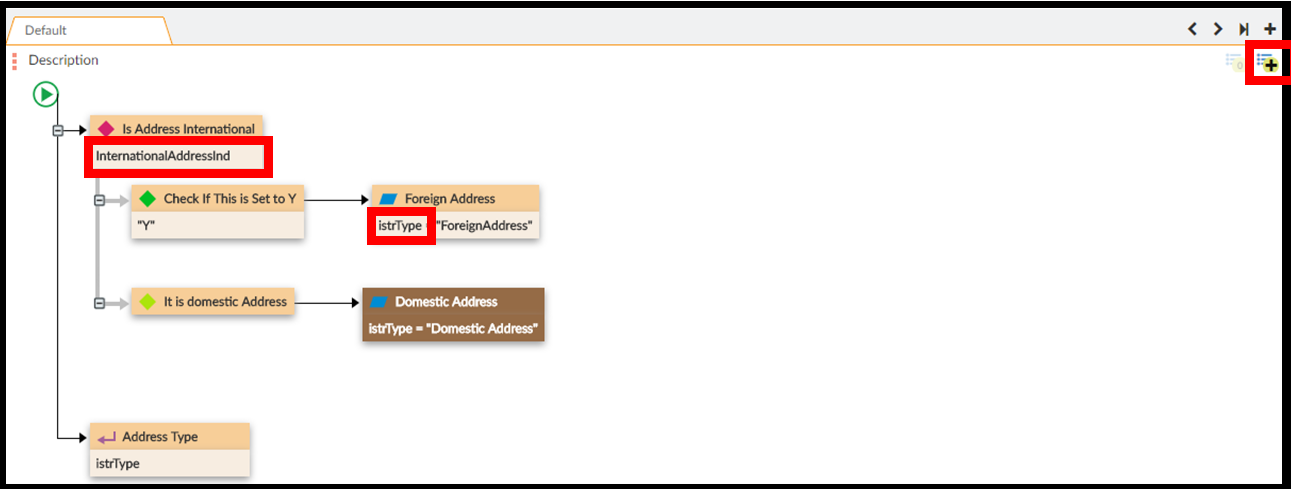
Step 5. Drag and drop the components of the rule.
S3 creates a new logical rule as an empty field. You must build the flowchart for the rule by dragging and dropping components from the Toolbox.
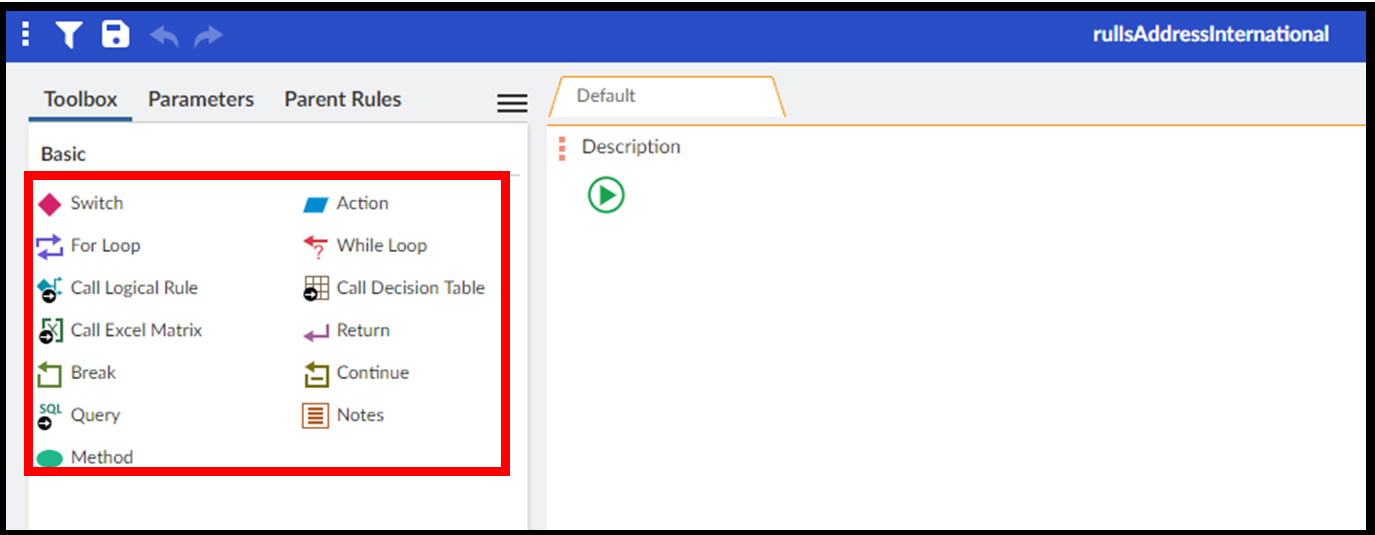
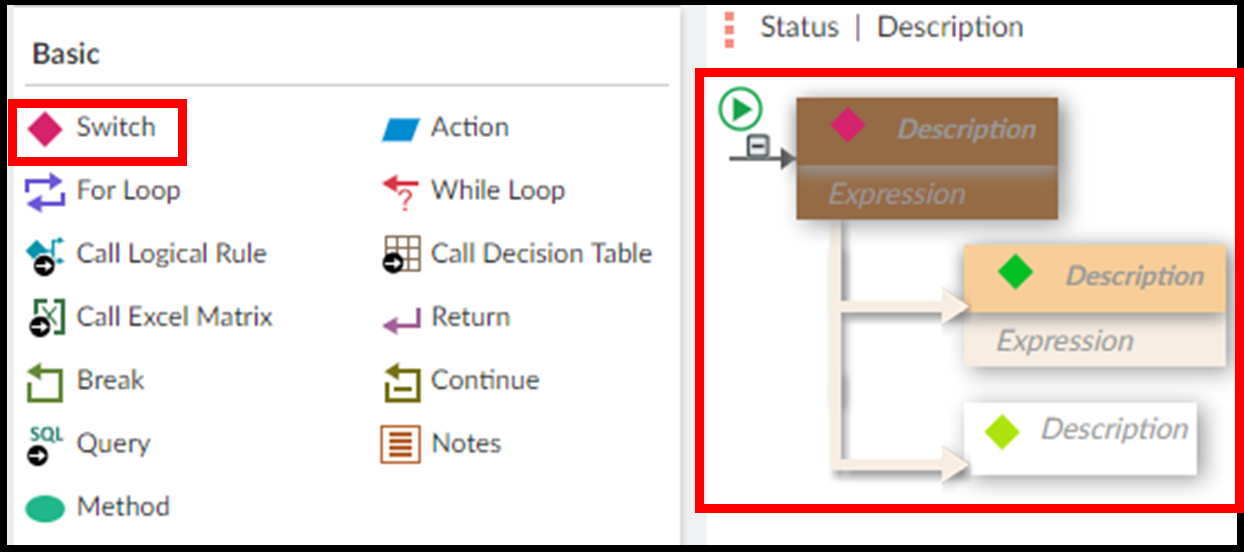
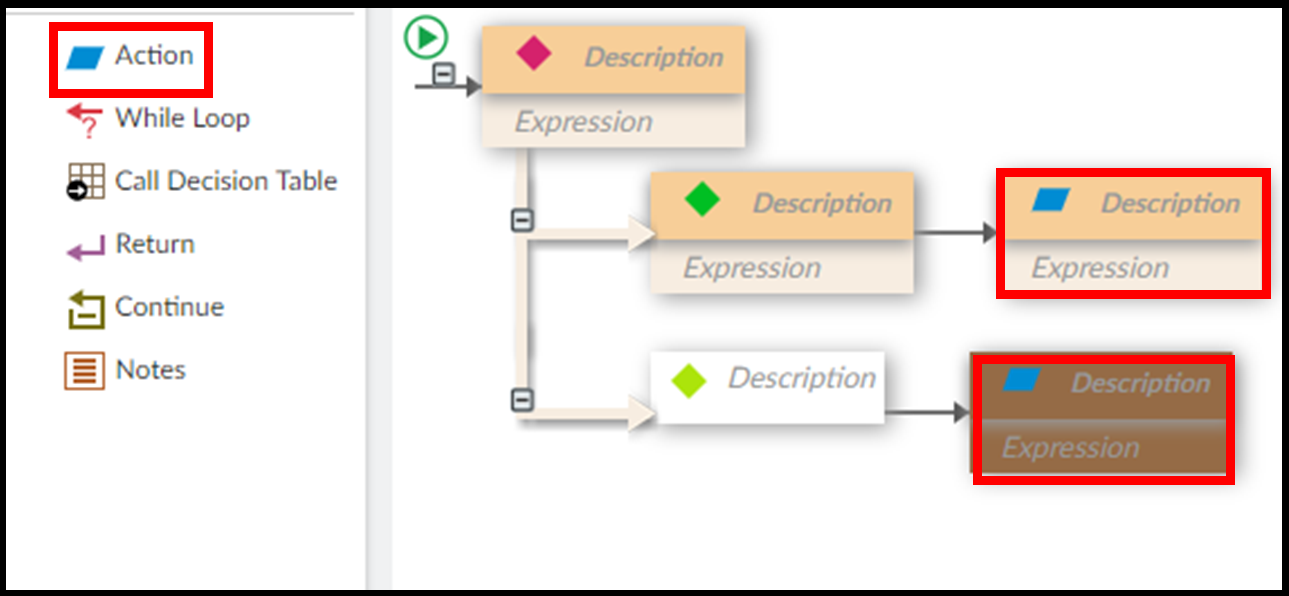
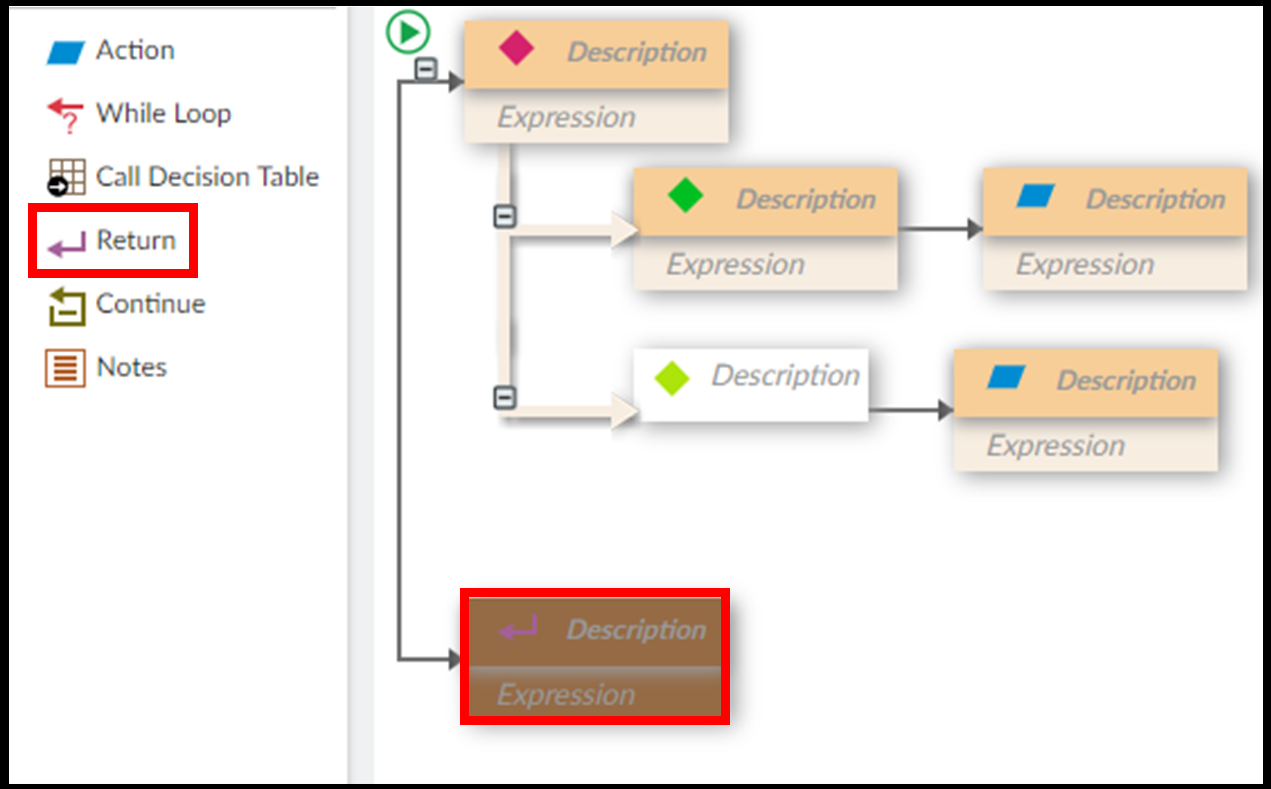
Step 6. Enter the description and expression for each component.
For each component, enter the description of what it does in the rule, then enter the expression. The is the actual logic the component executes.
There are two options for viewing your rule. In Developer View, descriptions and expressions both display. In Analyst View, only descriptions display. Always write descriptions so an Analyst can trace the rule without expressions.
It is possible for one person to create a rule in Analyst View with only description, and for another person to finish the rule later with the actual logic.
Step 7. Add variables.
Step 8. Enter the variable details.
Step 9. Click OK.
Step 10. Save the rule.
Click the Save icon.
Click the scenarios icon and select Add Scenario.
Step 13. Enter the Input Value and Expected Value.
Enter the input value and expected value for the test.
Step 14. Run the test.
Click the Run Test icon to run the test step.
This post is part of the Rules topic. Click here to open the Rules Overview.
#Develop
#Rules
#Task Steps
#Everyone
#Text Help